
Have you ever wondered how large organizations manage their complex financial structures and transactions within a single system? The answer lies in SAP, particularly through the use of company codes. These powerful organizational units simplify financial accounting, reporting, and regulatory compliance for businesses of all sizes. But what is a company code in SAP?
In this blog post, we’ll delve into the world of company codes in SAP, exploring their purpose, creation process, configuration, and integration with financial accounting. By the end of this post, you’ll have a solid understanding of the role company codes play in the SAP ecosystem and how they can streamline your organization’s financial management, as well as a clear answer to the question, “what is a company code in SAP?”
Key Takeaways
- Company codes in SAP provide a framework for the generation of financial statements at an independent entity level.
- Configuring and assigning company codes to other organizational units allows cost accounting, vendor management and compliance with legal requirements.
- Users can generate balance sheets for individual or multiple company codes using Financial Statement version in SAP.
Understanding Company Codes in SAP
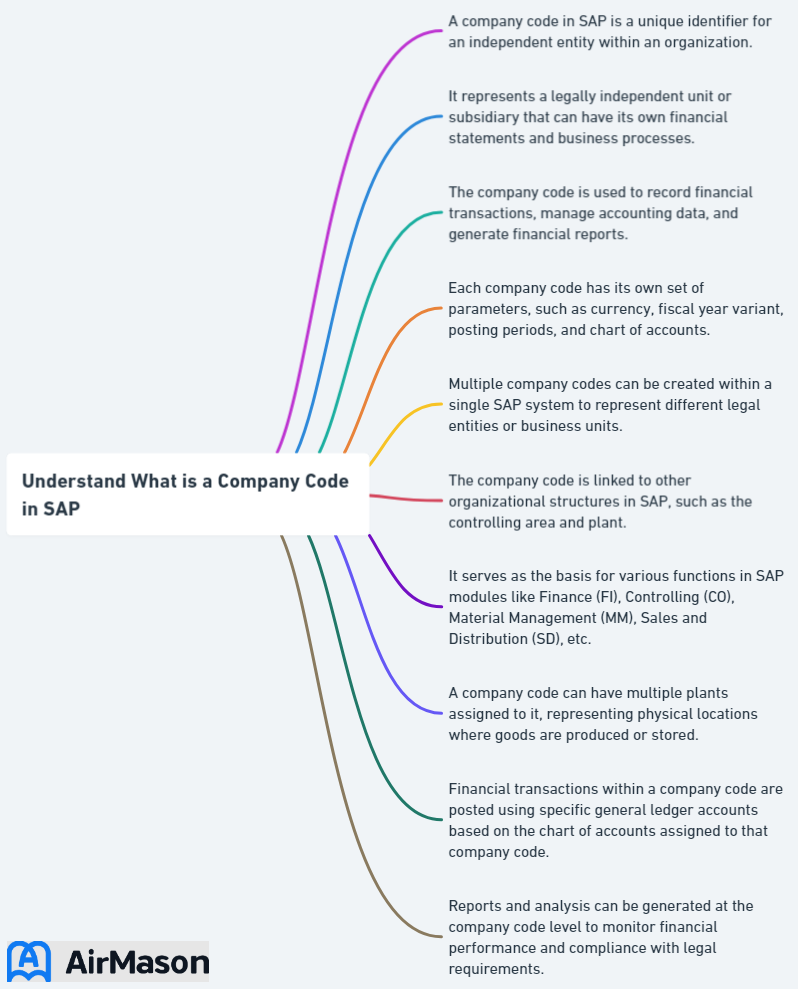
Company codes, representing a legal entity or a company, are pivotal in the SAP System’s external accounting. They assign all configurations and business processes to an independent accounting entity, thereby facilitating the generation of financial statements at the company code level. To put it simply, company codes are the backbone of financial accounting in SAP, allowing organizations to manage the accounts for several independent companies simultaneously.
These codes play an essential role in the enterprise structure, as they define legal entities or commercial places within the SAP system. Accurate tracking and reporting of financial transactions, compliance with accounting regulations, and informed business decision-making based on reliable financial information can be achieved through effective management of company code data by organizations.
Company Code Basics
A company code in SAP is the smallest organizational unit of external accounting, representing a legal entity within the SAP system and generating individual financial statements. It is the foundation for creating a complete, self-contained set of accounts, which is crucial for external reporting purposes and adherence to accounting regulations.
To define company code, it is necessary to provide relevant information, including the company name, address, and communication settings. Some common examples of how company codes are used in SAP include financial accounting, reporting, legal and regulatory compliance, organizational structure, controlling, intercompany transactions, and consolidation. In larger organizations, managing several company codes may be required for efficient operations.
Company Code Level
In the context of SAP Finance transactions, company codes symbolize the external accounting system as central organizational units. At least one company code (per client) is necessary for the implementation of the Financial (FI) component in SAP ERP Financials. It’s worth noting that there is no upper limit to the number of company codes that can be employed in SAP ERP Financials, giving organizations the flexibility to create as many company codes as required.
Company codes in SAP finance transactions have a significant influence on data segregation, facilitating the division and organization of financial data based on disparate legal entities or business units within an organization. This segregation ensures that financial transactions and data are kept distinct and separate for each company code, allowing for accurate reporting, analysis, and compliance with legal and regulatory requirements.
Code of Conduct Examples
When implementing a code of conduct within an organization or community, it’s vital to provide clear and specific code conduct examples. These examples serve as practical illustrations of expected behaviors and standards, helping individuals understand how to uphold the values and principles outlined in the code. For instance, a code of conduct may specify that disrespectful language or discriminatory remarks are not acceptable during discussions or meetings. Additionally, it might highlight the importance of maintaining confidentiality when dealing with sensitive information. By including concrete code conduct examples related to communication, collaboration, respect, and integrity, organizations can ensure that everyone comprehends the behavioral expectations and contributes to a positive and inclusive environment. Moreover, these examples help in fostering a culture of accountability and promoting a sense of responsibility among all stakeholders.
Creating a New Company Code in SAP

A series of steps are involved in creating a new company code in SAP, which includes accessing transaction codes, inputting necessary details, and saving and updating changes. The process ensures that your organization’s financial accounting system is set up correctly and tailored to the unique needs of each individual company code.
The subsequent sections will guide you through the procedure of creating a new company code in SAP and elucidate the process of configuring and delegating company codes to other organizational units like business areas and purchasing organizations.
Accessing Transaction Codes
To create a company code, users must access the appropriate transaction code, such as OX02, in SAP. Transaction codes are alphanumeric codes employed to access particular functions or processes within the SAP system. They serve as a convenient and expeditious way to navigate to different applications or execute predefined tasks, including managing an existing company code.
Users can access the configuration setup to create company code by inputting the OX02 transaction code in the command field. After accessing the transaction code, users can proceed to enter the required details for the new company code and check company code for accuracy.
Entering Required Details
While creating a new company code, it’s imperative for users to input pertinent details such as the company name, address, and communication settings. Providing accurate and up-to-date information is essential, as it defines the basic information and contact details of the company, which is utilized for various purposes, including financial accounting, reporting, and communication with external parties.
The required fields to be populated when entering the company address in SAP are:
- Street
- City
- Postal code
- Country
Ensuring that these fields are filled out accurately will help guarantee that your organization’s financial transactions and reports are precise and reliable.
Saving and Updating Changes
After entering the required information, users must follow these steps to create a new company code in SAP:
- Access the Change View Company Code screen.
- Select ‘New Entries’ to create a new company code.
- Input the requisite information and configure the settings.
- Press the ‘Save’ button.
Saving and updating changes finalize the creation of the new company code and ensure the SAP system aligns with your organization’s financial accounting requirements and stays current.
Configuring and Assigning Company Codes

Upon creating a company code, the ensuing step involves configuring and assigning the company codes to other organizational units, like business areas and purchasing organizations. This process involves linking company codes to these units, facilitating data transfer and streamlining business processes for efficient financial management.
In the following sections, we’ll discuss the process of assigning business areas and linking purchasing organizations to company codes, ensuring that your organization’s financial accounting system is configured correctly and tailored to the unique needs of each business unit.
Assigning Business Areas
Business areas can be assigned to company codes to facilitate data transfer and streamline business processes. By assigning business areas to company codes, organizations can track financial transactions and reporting for distinct segments of the organization, enabling more precise analysis and reporting based on different business areas within the company.
Some advantages of assigning business areas to company codes in SAP include:
- Cross-company code cost accounting
- Differentiation of transactions
- Consistency across company codes
- Easy configuration
Assigning business areas to company codes is a straightforward configuration process in SAP, making it effortless to set up and manage.
Linking Purchasing Organizations
Purchasing organizations can also be linked to company codes for efficient data transfer and procurement management. Linking purchasing organizations to company codes establishes a relationship between the purchasing organization and the company code, enabling better control and management of procurement activities within the organization.
Some advantages of connecting purchasing organizations to company codes for procurement management include:
- Streamlined procurement processes
- Improved cost control
- Enhanced vendor management
- Centralized reporting and analytics
- Compliance and governance
To link a purchasing organization to a company code in SAP, users can navigate to the transaction code ‘OX01’ or follow the path:
- Enterprise Structure
- Assignment
- Materials Management
- Assign Purchasing Organization to Company Code
Managing Company Code Data

As an organization progresses, managing and updating company code data in SAP becomes vital to ensure precise financial reporting and informed decision-making. To edit company code data, it involves editing address details and adjusting communication settings, as needed.
In the following sections, we’ll discuss how to edit address details and adjust communication settings for a company code in SAP, ensuring that your organization’s financial accounting system remains up-to-date and accurate.
Editing Address Details

Users can edit address details for a company code in SAP by following these steps:
- Access the pertinent transaction code.
- Locate the address details that need to be edited.
- Modify the necessary information.
- Save the changes.
By following these steps, users can ensure that the address details in SAP are accurate and up-to-date.
When editing address details in SAP company code, the available fields may include:
- Street address
- City
- Postal code
- Region
- Country
Regularly updating these fields helps guarantee that your organization’s financial transactions and reporting are precise and reliable.
Adjusting Communication Settings
Communication settings, such as email and phone numbers, can also be adjusted for a company code in SAP. These settings play a crucial role in managing SAP company codes, as they enable control of inbound and outbound call functions through SAP Collaboration Window, such as making and receiving calls by mouse-click.
To reset communication settings in SAP for a specific company code, users should follow these steps:
- Navigate to the relevant transaction code for communication settings from the SAP menu.
- Enter the system instance ID of the communication system they wish to set up communication arrangements with.
- Select the code for the specific company code they want to reset the communication settings for.
Ethics Program
An ethics program is an essential component within organizations, aiming to cultivate a culture of moral and responsible behavior among employees. This program outlines a set of principles, guidelines, and standards that guide decision-making and conduct within the workplace. The ethics program typically addresses various aspects, including appropriate behavior, conflicts of interest, confidentiality, compliance with laws and regulations, and the company’s values. By establishing an ethics program, organizations demonstrate their commitment to operating with integrity and ensuring that employees are aware of the expected ethical conduct. It serves as a framework for fostering trust, promoting accountability, and upholding the organization’s reputation in the business environment.
Implementing Company Codes in Financial Accounting

The implementation of company codes in financial accounting entails the generation of financial reports and the creation of balance sheets for precise financial management. By incorporating company codes into financial accounting, organizations can ensure that their financial transactions are accurately tracked and reported, adhering to legal and regulatory requirements. This process includes the use of a financial accounting component that streamlines the management of company codes.
In the following sections, we’ll discuss how to generate financial reports and create balance sheets using company codes in SAP, providing a comprehensive view of your organization’s financial status.
Generating Financial Reports
Company codes are crucial for generating financial reports in SAP, as they provide the necessary structure and data for accurate reporting. The Financial Statement version is a tool in SAP that facilitates the generation of financial reports for a company code, allowing users to create balance sheets, profit and loss statements, and other financial documents.
To generate financial reports using company codes in SAP, users must follow these steps:
- Access the Financial Statement version for the desired company code.
- Define the organizational unit for which they want to generate the report (e.g., whole group, individual company code).
- Record all pertinent transactions.
- Produce supporting documents such as balance sheets and profit and loss statements.
- Evaluate the generated financial reports.
Creating Balance Sheets
Balance sheets can also be created using company codes in SAP, providing a comprehensive view of a company’s financial status. In order to create a balance sheet in SAP, it is essential to have the General Ledger (GL) account master data, Chart of Accounts (COA), and financial statement forms or reports for balance sheets.
By accessing the SAP Easy Access screen and utilizing the applicable application to display the balance sheets for the company codes, users can generate either separate balance sheets for each company code or aggregated balance sheets for multiple company codes.
Code of Conduct Violations
Code of conduct violations refer to breaches of established guidelines and ethical principles within a specific organization, community, or social setting. These violations can encompass a wide range of behaviors that contravene the prescribed rules of conduct, which are in place to maintain order, fairness, and a conducive environment for all involved parties. Such breaches may involve actions such as harassment, discrimination, dishonesty, bullying, or other actions that go against the stated principles and values of the respective entity. Addressing code of conduct violations is crucial to uphold the integrity and reputation of the organization, protect individuals from harm, and ensure a harmonious and respectful environment for all members. Proper protocols for reporting, investigating, and responding to these violations are essential to uphold the standards of behavior and maintain a healthy, inclusive atmosphere.
Summary
In conclusion, company codes in SAP play a vital role in simplifying financial accounting, reporting, and regulatory compliance for organizations of all sizes. By creating, configuring, and managing company codes, businesses can ensure accurate tracking and reporting of financial transactions, guarantee compliance with accounting regulations, and make informed decisions based on reliable financial information.
As you embark on your journey with SAP, remember that company codes are the foundation of your organization’s financial accounting system. By understanding and utilizing company codes effectively, you can streamline your financial management processes and drive your organization towards greater success.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is client and company code in SAP?
The client in SAP is the highest level in the system hierarchy and all data stored at that level can be accessed by all company codes. On the other hand, the company code is an organizational unit of external accounting within the SAP System.
What is company code vs business area in SAP?
Company Codes are used to distinguish accounting areas within a business while Business Areas allow for an additional level of control over cost and revenue allocations. Business Areas may cross multiple Company Codes, representing various responsibility areas within a business. Configuration of Business Areas is optional.
What is company code in SAP interview questions?
Company Code in SAP is the smallest organizational unit of external accounting for which financial statements can be created and transactions can be posted.
What is the company code field in SAP table?
The company code field in SAP Table T001 is accessed through transaction code OX02, which is an integral part of the SAP Financial Accounting framework.
Where is the company code in SAP?
The company code in SAP can be found by going to IMG => Enterprise Structure => Definition => Financial Accounting and entering Transaction Code OX02. Then, click on the ‘New Entries’ Button and maintain the details for the new company code.