
As an employer, knowing the precise employee handbook requirements by state is essential to ensure compliance and legal protection. This article serves as your resource for understanding these diverse state mandates, tailored to help you confidently shape your employee handbook according to your state’s specific laws.
Key Takeaways
- Employee handbooks must reflect state-specific laws including differences in minimum wage, overtime regulations, anti-discrimination and harassment policies, family and medical leave, and workplace safety to ensure legal compliance and set clear employee expectations.
- Essential components of a legally compliant employee handbook involve aligning with both federal and state laws, clear communication of policies, and regular updates to adapt to new legal changes and workplace trends like remote work and diversity.
- Multi-state employers face particular complexities and should ensure compliance with all state-specific employment laws by creating customized addendums to a central handbook, conducting regular reviews, subscribing to legal update services, and seeking legal advice.
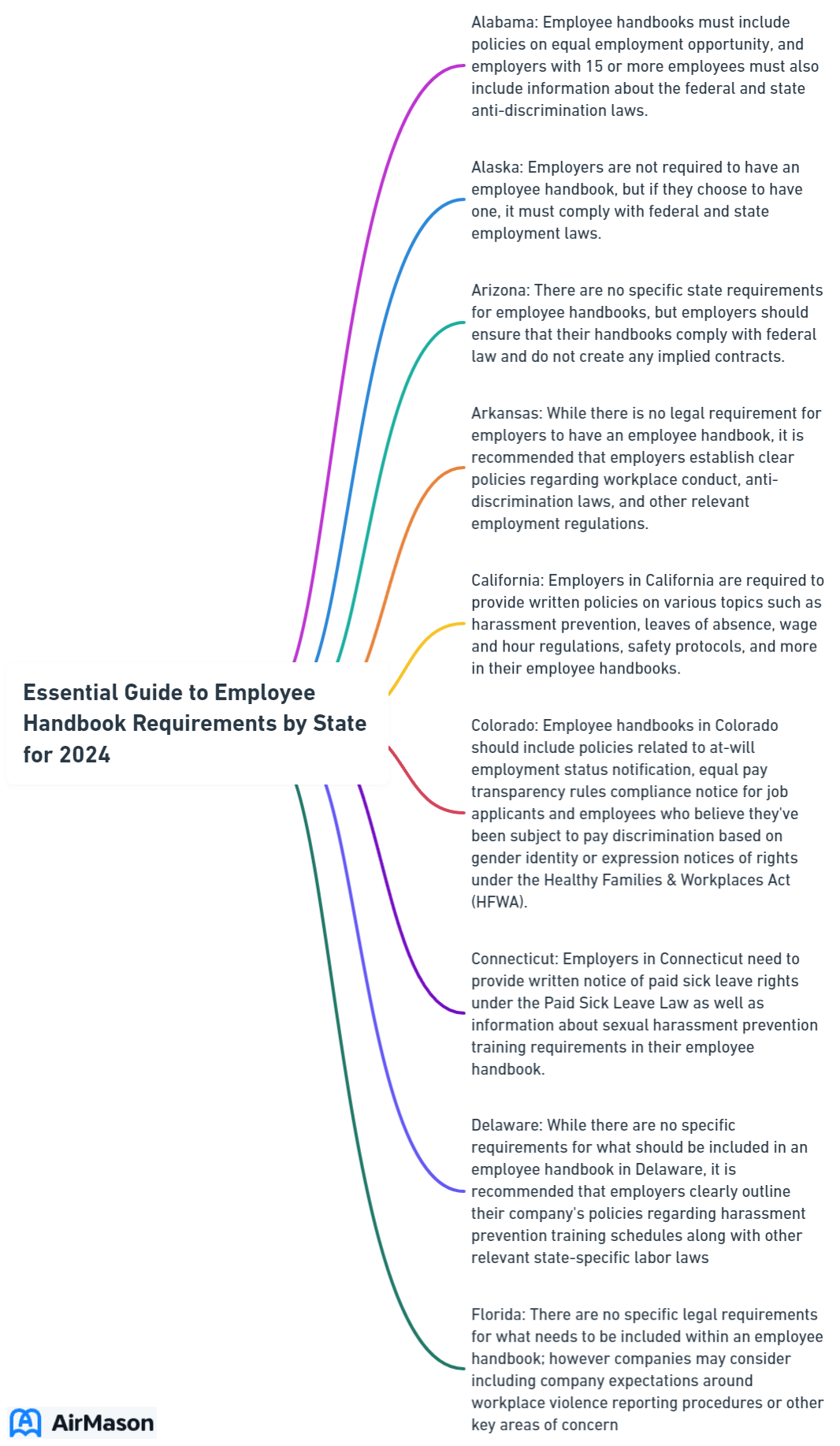
Employee Handbook Importance
Understanding the employee handbook importance is paramount for any organization. The “Employee Handbook Importance” cannot be overstated, as it serves as a comprehensive guide outlining company policies, procedures, and expectations. This document not only communicates the company’s values and culture but also helps in mitigating legal risks by clearly defining employee rights and responsibilities. Moreover, it ensures consistency in decision-making processes and fosters transparency within the workplace. By providing employees with a centralized resource, the handbook promotes clarity and reduces misunderstandings, thereby enhancing overall productivity and organizational cohesion. In essence, recognizing and adhering to the “Employee Handbook Importance” is foundational for cultivating a positive and compliant work environment.
Understanding State-Specific Employee Handbook Requirements

The landscape of employment laws and regulations is as diverse as the 50 states themselves. Whether it’s minimum wage, overtime regulations, anti-discrimination, or harassment policies, every state has distinct stipulations. An effective employee handbook must reflect these state-specific guidelines to foster clarity and consistency across the organization, upholding professionalism and maintaining legal compliance.
Given the intricacies of state laws and regulations, crafting a comprehensive employee handbook that meets all state requirements can be a daunting task. Remember, these handbooks are more than just a legal safety net; they function as an essential instrument for setting clear employee expectations, defining the employment relationship, and fostering a harmonious workplace environment through well-crafted employee handbook policies.
Labor Laws and Regulations
Delving into the specifics, labor laws and regulations significantly vary from one state to another. For instance, states like Colorado have distinct minimum wage and overtime regulations compared to other states. Grasping these specific state requirements is of paramount importance to employers in order to steer clear of legal issues and guarantee compliance.
The realm of anti-discrimination laws also illustrates this diversity. States like California, New York, and Illinois offer comprehensive protections, including employment, housing, and public accommodations for LGBTQ+ individuals, while others such as Indiana, Texas, and Alabama may offer more limited protections. This wide variation necessitates tailored policies in multi-state employee handbooks.
Family and Medical Leave Policies

The disparities extend to family and medical leave policies as well. While the Federal Family and Medical Leave Act (FMLA) allows eligible employees to take up to 12 weeks of unpaid leave for certain family and medical reasons, state laws often offer additional protections. As of 2024, the following states and Washington, D.C., have enacted laws providing for paid family and medical leave, with coverage encompassing employers of all sizes:
- California
- Connecticut
- Massachusetts
- New Jersey
- New York
- Oregon
- Rhode Island
- Vermont
- Washington
- Colorado
- Maine
These laws encompass a wide range of leave types, including:
- medical leave
- parental leave
- caregiving leave
- deployment-related leave
- safe leave for victims of domestic or sexual violence
Considering the disparities in access to short-term disability coverage, particularly among low-income and part-time workers, employers must include clear medical and family leave policies in employee handbooks to align with federal and state regulations.
Workplace Safety and Health Standards
When it comes to workplace safety and health standards, state-specific regulations come into play once more. There are 22 states with OSHA-approved State Plans covering most private sector workers and all state and local government workers. Employers are obliged to adhere to both federal OSHA regulations and state-specific safety and health standards in these states.
State Plans must have standards and enforcement programs that are as effective as federal OSHA, with the potential for having different or additional requirements. This underscores the necessity of state-specific policies in employee handbooks to maintain compliance with both federal and state safety and health standards.
Employee Handbook for Non-Profit
The employee handbook for non-profit organizations serves as a vital resource for employees, outlining policies, procedures, and expectations specific to the non-profit sector. This comprehensive guide provides valuable information on organizational values, code of conduct, benefits, and employment policies tailored to the unique needs of non-profit employees. By familiarizing themselves with the contents of the employee handbook, staff members can better understand their roles, responsibilities, and rights within the organization, fostering a positive and productive work environment.
Key Components of a Compliant Employee Handbook

Beyond understanding state-specific requirements, there are key components that contribute to a legally compliant and effective employee handbook. These components include legal compliance, clear policy communication, and regular updates. Fundamentally, an employee handbook is not just a document; it is a key instrument outlining policies, procedures, and expectations, and serves as a reference point for both employees and employers.
A well-crafted handbook promotes a work environment where:
- Compliance is maintained, thereby mitigating legal risks for the company
- Job satisfaction and morale are enhanced by keeping employees well-informed about company guidelines
- A sense of transparency and trust is fostered
Legal Compliance
Legal compliance forms the backbone of an effective employee handbook. This involves adhering to federal and state laws, including the National Labor Relations Act, anti-discrimination policies, and recent legislative changes. For instance, the NLRB ruling on Stericycle, Inc., highlighted the need for documentary evidence justifying work rules, indicating the importance of legal compliance in handbook policies.
Moreover, the landscape of federal laws is constantly evolving, with recent changes necessitating updates in non-discrimination policies in handbooks without reference to specific genders. The Ending Forced Arbitration in Sexual Assault and Sexual Harassment Act also requires revision of arbitration clauses, indicating that such issues cannot be covered by forced arbitration in handbooks.
Anti-discrimination policies and an ADA accommodation policy must be explicitly included, detailing the employer’s process for providing reasonable accommodations and engaging in the interactive process.
Clear Communication
Clear communication is a cornerstone of an effective employee handbook. It ensures that employees understand and apply company policies, fostering a compliant and professional workplace. Adapting the employee handbook to suit the specific needs of the business and effectively conveying policies are vital elements in the creation or update of the handbook.
Using clear language and providing relevant examples or scenarios facilitates employee understanding and correct application of policies in daily work. Establishing a fair and transparent disciplinary process that is consistently applied to all employees is essential for maintaining legal compliance and trust within the workplace.
Regular Updates
Regular updates are critical to keeping employee handbooks relevant and compliant. A regular review and update of the employee handbook aids in maintaining alignment with legal requirements and industry best practices. Conducting an annual review is pivotal, and if laws change mid-year, employers must promptly update and confirm employees are informed and have acknowledged the changes.
Moreover, employers need to develop new policies in response to trends like:
- remote work
- diversity
- pay practices
- health policies such as those for contagious diseases like COVID-19
The employee handbook should be easily accessible to employees, with clear guidance on how to access it, and include the latest revision dates and an organizational chart.
Addressing Unique State Employment Laws

Unique state employment laws present a further layer of complexity for state laws employers. These may include changes such as:
- California’s new paid sick leave laws
- Massachusetts’ Paid Family Leave amendments
- Illinois’ broad paid leave requirements
- Michigan’s protection for sexual orientation and gender identity
To navigate this complexity, employers should seek legal advice when updating their handbooks.
As local employment laws evolve, like Seattle’s ban on caste discrimination and Utah’s limitations on using vaccination status, legal consultation is critical for ensuring handbook policies remain compliant. This is where grasping unique state employment laws becomes significant, necessitating employers to update their handbooks accordingly for compliance maintenance.
Pay Transparency Policies
Pay transparency policies are a good example of unique state employment laws that require attention. As of early 2023, 10 states in the United States have enacted pay transparency laws, including:
- California
- Colorado
- Connecticut
- Hawaii
- Illinois
- Maryland
- Nevada
- New York
- Rhode Island
- Washington
These laws vary, with some states requiring disclosure of salary ranges during the hiring process, upon request, or when changing positions. In California and Colorado, employers are obliged to include salary ranges in job postings and to current employees upon request. To meet pay transparency requirements, pay policies in employee handbooks must be regularly revisited and updated, taking into account state-specific laws, the effect of inflation, and the need for clear disclosure of compensation ranges.
Marijuana Use and Testing Guidelines
Marijuana use and testing guidelines also differ by state and have significant implications for employee handbooks. Employers need to address changes in marijuana/drug use and testing policies, given the legalization in numerous states, potential changes in federal scheduling decisions, and possible mental health concerns.
For instance, California employers are barred from discriminating against workers for cannabis use outside of work and cannot ask about such use. Employers are also prohibited from using the results of marijuana detected through hair or urine tests in hiring, firing, or penalizing workers, while allowing other tests like blood tests to detect impairment.
It’s important to note that there are exceptions to these rules, further emphasizing the need for state-specific guidelines in employee handbooks.
Dress Code and Appearance Policies
Dress code and appearance policies further illustrate the variances in state employment laws. As of 2024, 20 states, including Minnesota, have enacted the CROWN Act to prohibit discrimination based on hair texture or hairstyles typically associated with race or national origin. Over 40 local governments have also established laws similar to the CROWN Act, further prohibiting discrimination based on hair texture and style.
Employers in places with the CROWN Act must review and update their employee handbooks, training materials, and appearance policies to ensure compliance with these anti-discrimination laws. Even in jurisdictions without specific CROWN Act laws, employers must ensure equal application of dress codes and grooming policies without any form of discrimination, adhering to all applicable laws.
Navigating Employee Handbooks for Multi-State Employers

For multi-state employers, the task of maintaining compliant employee handbooks can be even more challenging. These employers must navigate the complexities of different state-specific employment policies, often requiring a centralized or master employee handbook with state-specific addendums to manage the legal landscape while maintaining organizational consistency.
Regular reviews of employee handbooks are necessary to ensure they remain compliant with changes to laws and regulations such as:
- minimum wage
- overtime
- paid leave
- anti-discrimination laws
It is advisable for employers to conduct annual reviews of handbooks, ideally on a quarterly basis, and consistently evaluate policy effectiveness.
Staying Informed
Staying informed about changes in state-specific employment laws is critical for multi-state employers. Regular monitoring of these changes ensures that employee handbooks remain compliant and up to date.
Subscribing to reliable legal resources or services that track employment law updates can be extremely beneficial. Services like SHRM’s Employee Handbook Builder offer regular alerts and updates that can help employers stay informed about both state and federal legislative changes.
Customizing Policies by State
Customizing policies by state is another crucial aspect of maintaining compliant employee handbooks. This involves researching specific state labor laws, such as those governing:
- minimum wage
- overtime
- paid leave
- anti-discrimination
and tailoring the handbook accordingly, including guidelines for personal devices.
With the rise of remote work, employers must also evaluate and potentially customize remote work policies in the handbook to establish:
- Boundaries
- Expectations
- Data security protocols
- Compliance with FLSA for all employees, including those working remotely from different states.
Seeking Legal Advice
Legal advice is fundamental in ensuring compliance and mitigating potential legal risks associated with employee handbooks. It is advisable for employers to seek legal counsel during the review and update of their handbooks to ensure compliance with both federal and state laws.
Working with legal professionals specializing in employment law can be a proactive measure that helps mitigate potential legal risks. Legal counsel can also assist employers in drafting privacy and confidentiality policies within the employee handbook that comply with various state regulations.
Resources for State-Specific Employee Handbook Information
Several resources are available to provide valuable information and guidance on state-specific employee handbook requirements, making the task of maintaining compliant handbooks less intimidating. The Society for Human Resource Management (SHRM), for instance, offers a comprehensive guide for developing handbooks, including sample handbooks and a form for the Acknowledgement of Receipt tailored to state-specific requirements.
Other resources include law firms and online platforms that publish updates and articles on state-specific employee handbook requirements. These resources, such as JD Supra and the Employment Law Information Network, offer valuable information for employers and help them stay informed and compliant.
Summary
In conclusion, understanding state-specific employee handbook requirements is crucial for legal compliance and effective communication within an organization. For multi-state employers, this task can be particularly challenging, necessitating regular updates, clear communication, and legal counsel. However, with the right resources and a proactive approach, employers can successfully navigate the complexities of state-specific employment laws and maintain compliant, effective handbooks that promote a harmonious and professional workplace.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is legally required to be in an employee handbook?
An employee handbook should include legally required topics such as minimum wage and overtime regulations, anti-discrimination and harassment policies, family and medical leave policies, safety and health regulations, and time off and paid leave policies. Additionally, it should cover the employer’s mission statement, equal employment opportunity statement, contractual disclaimer, and at-will employment statement.
Do employment laws differ by state?
Yes, employment laws do differ by state due to the rights of states to govern themselves, leading to variations in labor laws such as minimum wage. For example, while the federal minimum wage is $7.25 an hour, some states have a higher minimum wage.
What should not be included in an employee handbook?
Employee handbooks should not include any discriminatory policies or language. It’s important to ensure that all content is in compliance with labor laws and regulations.
How often should an employee handbook be updated?
You should update your employee handbook annually to reflect any changes in the law and your company’s practices. This helps ensure that your policies remain current and compliant.
Why is clear communication important in an employee handbook?
Clear communication in an employee handbook is important because it helps employees understand and apply company policies effectively, fostering a compliant and professional workplace.
Important Disclaimer:
Please be aware that the content on this page has been generated by using artificial intelligence language models and may contain errors, inconsistencies, or outdated information. It is provided as-is without any warranties or guarantees of accuracy.
We strongly recommend using this content as a starting point for further research. We disclaim any liability for damages or losses resulting from the use or reliance on this content.