
In today’s diverse and complex world, it’s more important than ever to ensure that our workplaces are inclusive and respectful to all employees, regardless of their background or characteristics. Tackling discrimination and harassment in the workplace is a critical aspect of creating an environment where everyone can thrive and contribute to their full potential. But how do we effectively address these issues in 2023?
In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the various types and forms of discrimination and harassment, the legal framework for addressing these issues, how to identify and prevent such behavior, and what steps employers and employees can take to resolve these situations and create a more inclusive workplace.
Key Takeaways
- Understanding discrimination and harassment in the workplace is essential to recognizing and rectifying these behaviors.
- Employers have a responsibility to proactively prevent and address workplace discrimination, while employees have the right to be free from it.
- Reporting incidents of discrimination or harassment involves filing a complaint with the EEOC, participating in alternative dispute resolution processes, and seeking protection from retaliation for reporting or participating in investigations.
Understanding Discrimination and Harassment
Discrimination and harassment in the workplace come in many forms and can have a profound impact on employees’ well-being and job performance. In a nutshell, discrimination occurs when an employee or job applicant is treated unfavorably due to their membership in a protected group, such as:
- race
- color
- religion
- sex
- national origin
- age
- disability
Harassment is a form of employment discrimination, which violates several federal laws, such as Title VII of the Civil Rights Act of 1964, the Age Discrimination in Employment Act of 1967, and the Americans with Disabilities Act of 1990. Legal action can be taken against harassment based on these laws.
A thorough understanding of the different types of discrimination and harassment that can occur in the workplace is key to addressing these issues effectively. This knowledge enables us to recognize such behaviors promptly and take the necessary steps to foster an inclusive and respectful work environment.
Discrimination and Harassment
Discrimination and harassment are grave issues that plague various sectors of society, including workplaces, educational institutions, and public spaces. The impact of discrimination and harassment is profound, affecting individuals physically, emotionally, and psychologically. Discrimination is the unjust or prejudicial treatment of individuals or groups based on characteristics such as race, gender, religion, sexual orientation, or socioeconomic status. Harassment involves unwanted and offensive behavior, including verbal, physical, or visual actions, that create an intimidating, hostile, or demeaning environment for the victims. Combating discrimination and harassment requires proactive efforts, encompassing education, policy development, and a collective commitment to fostering inclusivity and respect for all. Addressing these issues effectively is crucial for promoting equality, diversity, and a healthier, more harmonious soc
Types of Discrimination
Discrimination can manifest in various ways, affecting individuals based on different protected characteristics. For example:
- Title VII of the Civil Rights Act of 1964 prohibits discrimination based on race, color, religion, sex, and national origin.
- The Americans with Disabilities Act protects employees against discrimination based on disability.
- The Age Discrimination in Employment Act protects employees against discrimination based on age.
In addition to federal laws, state laws and regulations may provide further protections against discrimination. For instance, in California, the Labor Code prohibits discrimination based on:
- Marital status
- Sexual orientation
- Gender identity
- And other factors
Recognizing the diverse types of discrimination allows us to respond swiftly and appropriately if it occurs and to take preventive measures.
Forms of Harassment
Harassment in the workplace can take on many forms, including:
- Verbal harassment: offensive, intimidating, or hostile communication, such as name-calling, insults, and threats
- Physical harassment: unwanted physical conduct, ranging from pushing and shoving to more severe forms of aggression
- Visual harassment: displaying offensive images or making offensive gestures that create a hostile work environment.
The ability to recognize diverse forms of harassment is vital to addressing them effectively and maintaining a safe, respectful workplace. Being aware of the many ways harassment can manifest enables us to identify and respond to such behaviors more efficiently, fostering an environment where all employees can thrive.
Legal Framework for Addressing Workplace Discrimination and Harassment

Familiarity with the legal framework governing workplace discrimination and harassment is indispensable for addressing and preventing such conduct. Both federal and state laws and regulations have been enacted to protect employees and job applicants from unfair treatment based on their protected characteristics.
At the federal level, laws such as Title VII of the Civil Rights Act of 1964, the Americans with Disabilities Act, and the Age Discrimination in Employment Act serve to prohibit various forms of employment discrimination, ensuring equal opportunities for all. State laws, on the other hand, can provide additional protections beyond those established by federal laws, covering a wider range of protected characteristics or offering greater remedies for victims of discrimination.
A clear understanding of the legal framework surrounding workplace discrimination and harassment allows employers and employees to navigate these complex issues more effectively and take the necessary steps to address and prevent such behaviors.
Title VII of the Civil Rights Act of 1964

Title VII of the Civil Rights Act of 1964 is a cornerstone of anti-discrimination law in the United States. Discrimination in employment has no place. This includes discrimination based on race, color, religion, sex, and national origin. This legislation covers various aspects of employment, such as recruitment, termination, remuneration, and advancement opportunities, ensuring that all individuals are treated fairly and equitably in the workplace.
Both employers and employees need to grasp the protections and prohibitions under Title VII to comply with federal anti-discrimination laws and strive towards creating an inclusive workplace devoid of discrimination and harassment.
Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA)
The Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA) is another essential piece of legislation that addresses workplace discrimination. It prohibits discrimination based on disability and requires that reasonable accommodations be made for employees with disabilities. By providing these accommodations, employers can ensure equal access to opportunities and advantages of employment for individuals with disabilities.
Both employers and employees need to grasp the requirements of the ADA to ensure the workplace is inclusive and accessible for individuals with disabilities. Compliance with the ADA can help employers foster an environment where all employees, disability notwithstanding, can contribute to their full potential.
Age Discrimination in Employment Act (ADEA)
The Age Discrimination in Employment Act (ADEA) is designed to protect employees aged 40 and older from discrimination in the workplace based on their age. By prohibiting age-based discrimination, the ADEA ensures that older employees are not unfairly treated or excluded from employment opportunities due to their age.
Both employers and employees need to grasp the provisions of the ADEA to ensure an inclusive and age-respectful workplace. ADEA compliance allows employers to foster an environment where all employees, irrespective of age, can fully contribute and enjoy equal opportunities.
State Laws and Regulations
In addition to federal law, state and federal law regulations may offer additional protections against workplace discrimination and harassment. For example, the California Labor Code provides protections beyond those established by federal laws, covering a wider range of protected characteristics and offering greater remedies for victims of discrimination.
Employers and employees need to familiarize themselves with both federal and state laws to ensure compliance and protection against workplace discrimination and harassment. By understanding and adhering to legal guidelines, they can collectively work towards a more inclusive and respectful work environment, void of discrimination and harassment.
Anti Harassment Policy
An anti harassment policy is a fundamental component of any organization, underscoring the commitment to maintaining a safe and respectful environment for all individuals involved. This policy sets forth clear guidelines and expectations, defining what constitutes harassment and the consequences for such behavior. The aim is to prevent any form of discrimination, bullying, or unwelcome behavior that could adversely affect employees, clients, or stakeholders. By implementing a robust anti harassment policy, organizations can foster a culture of inclusivity and accountability, promoting collaboration and productivity while ensuring the well-being and dignity of all participants within the organization. It also demonstrates the organization’s dedication to upholding ethical and legal standards, thereby building trust and credibility both internally and externally.
Identifying Unlawful Discrimination and Harassment

Identifying unlawful discrimination and harassment in the workplace is a crucial step in preventing and addressing these issues. Unlawful discrimination is defined as treating someone differently or less favorably based on their protected characteristics, such as:
- race
- color
- religion
- sex
- national origin
- age
- disability
- genetic information
Effectively addressing discrimination and harassment requires an understanding of the concepts of disparate treatment, disparate impact, and hostile work environment.
Disparate Treatment and Disparate Impact
Disparate treatment and disparate impact are two forms of discrimination that can occur in the workplace. Disparate treatment refers to intentional discrimination, where individuals in a protected class are treated differently.
Disparate impact, on the other hand, refers to unintentional discrimination that results from policies or practices that have a disproportionately negative effect on members of protected classes, even without any intention to discriminate.
Understanding the differences between disparate treatment and disparate impact helps employers and employees identify instances of discrimination more effectively, thereby enabling appropriate action to address and prevent such behavior.
Hostile Work Environment
A hostile work environment is a form of harassment that occurs when unwelcome conduct creates an intimidating, oppressive, or uncomfortable work atmosphere. This can include:
- Discrimination or harassment
- Bullying or intimidation
- Excessive criticism from leaders or managers
- Sexual harassment
- Aggressive behavior from bosses or co-workers
Recognizing a hostile work environment is key to addressing and preventing such situations. Understanding how a hostile work environment can manifest allows employers and employees to collaborate in creating a more inclusive and respectful workplace.
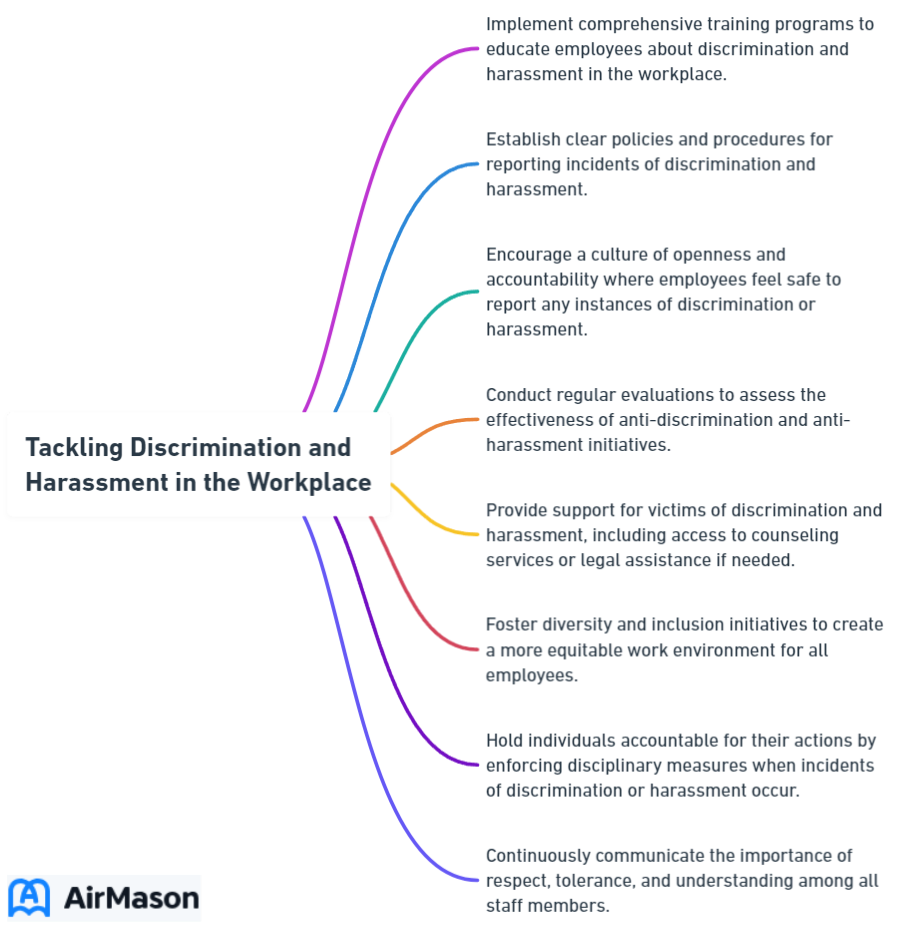
Preventing and Addressing Discrimination and Harassment

Preventing and addressing discrimination and harassment in the workplace is the responsibility of both employers and employees. Employers are responsible for stopping, addressing, and preventing harassment, while employees have the right to report incidents and participate in preventive or corrective measures related to workplace discrimination and harassment.
Understanding the responsibilities of both employers and employees in preventing and addressing discrimination and harassment is the key to creating a workplace where everyone is treated fairly and respectfully.
Employer Responsibilities
Employers have a responsibility to proactively prevent and address workplace discrimination and harassment by:
- Ensuring that managers understand their obligation to stop, address, and prevent harassment
- Implementing and enforcing anti-harassment policies and procedures
- Providing training and education on discrimination and harassment prevention
- Investigating and resolving complaints of discrimination and harassment promptly and objectively
- Taking appropriate disciplinary action against perpetrators of discrimination and harassment
- Cultivating a work environment that is free from discrimination and harassment.
Fulfilling their responsibilities allows employers to create a workplace where all employees feel safe, respected, and valued, thereby fostering a more inclusive and productive work environment.
Employee Rights and Responsibilities
Employees have the right to be free from discrimination and harassment in the workplace and have the responsibility to inform their employer of any incidents of discrimination or harassment. By reporting incidents and participating in preventive or corrective measures, employees play an essential role in maintaining a workplace that is free from discrimination and harassment.
When employees understand and exercise their rights and responsibilities, they contribute to a more inclusive and respectful work environment where everyone has the opportunity to thrive.
Reporting and Resolving Workplace Discrimination and Harassment

When instances of discrimination and harassment occur in the workplace, it’s important to know how to report and resolve these issues effectively. Employees who believe they have been discriminated against or harassed can:
- File a complaint with the Equal Employment Opportunity Commission (EEOC)
- Participate in alternative dispute resolution processes
- Seek protection from retaliation for reporting or participating in investigations of workplace discrimination and harassment.
Sexual Harassment Policy
A sexual harassment policy is an essential component of any organization’s commitment to maintaining a safe and respectful work environment. A well-crafted sexual harassment policy outlines the company’s stance on this critical issue and provides clear guidelines on what constitutes sexual harassment, how to report incidents, and the consequences for offenders. Such policies are designed to protect employees from any form of unwelcome sexual advances, comments, or conduct that creates a hostile or intimidating workplace. Additionally, a sexual harassment policy communicates the organization’s dedication to fostering inclusivity and preventing discrimination, helping to ensure that all employees can perform their duties free from harassment and fear of reprisal. Regular training and awareness campaigns on the sexual harassment policy are vital to guarantee its effectiveness in preventing and addressing such behaviors in the workplace.
Filing a Complaint with the Equal Employment Opportunity Commission (EEOC)
The process for filing a complaint with the EEOC involves contacting an EEO Counselor, completing counseling, submitting a formal complaint, and undergoing an investigation by the EEOC. Employees should be prepared to provide detailed information about the discrimination or harassment they have experienced, including dates, times, locations, and specific occurrences, as well as the names and contact information of any witnesses or individuals who may have pertinent information.
Filing an employment discrimination complaint with the EEOC enables employees to protect their rights and ensure that appropriate action is taken to address and prevent further instances of discrimination and harassment.
Alternative Dispute Resolution
Alternative dispute resolution (ADR) can be a valuable tool for resolving workplace discrimination and harassment issues outside of the formal legal process. ADR techniques, such as mediation, allow disputants to reach an agreement with the help of a certified and impartial third party, without the need for a formal trial or hearing. Through ADR, employees and employers can often resolve issues more quickly and cost-effectively than through traditional litigation.
Considering alternative dispute resolution options allows employees and employers to collaboratively and efficiently address workplace discrimination and harassment.
Retaliation Protections
Employees who report or participate in investigations of workplace discrimination and harassment are protected from retaliation under both federal and state laws. Retaliation can take many forms, such as termination, demotion, or other negative job actions.
Understanding and exercising their rights to retaliation protections empowers employees to confidently report incidents of discrimination and harassment, contributing to a more inclusive and respectful work environment.
Awareness of the legal protections against retaliation gives employees a sense of security when reporting incidents of discrimination and harassment, knowing they are protected from adverse consequences.
Summary
In conclusion, tackling discrimination and harassment in the workplace in 2024 is a collaborative effort between employers and employees. Understanding the different types and forms of discrimination and harassment, the legal framework governing these issues, and the responsibilities of employers and employees in preventing and addressing such behavior is essential in creating an inclusive and respectful work environment for all.
By working together to address and prevent discrimination and harassment, we can create a workplace where everyone is treated fairly and with respect, ensuring that all employees have the opportunity to contribute to their full potential and succeed in their careers.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is discrimination and harassment in the workplace?
Workplace discrimination and harassment is any form of unwanted conduct related to a person’s race, color, religion, gender, national origin, age or disability, such as offensive jokes, objects, pictures, name calling, physical assaults and threats.
What is an example of discrimination and harassment?
Discrimination and harassment in the workplace can take many forms, such as derogatory jokes, racial slurs, personal insults, and expressions of intolerance. This type of abuse can range from mocking a worker’s accent to making threats or displaying discriminatory symbols.
What 3 factors determine workplace harassment?
Workplace harassment is largely dependent on three factors; whether the victim tolerated the harassment to keep their job, whether it created a hostile work environment and if the harassment was in response to filing a complaint.
What are 3 things that an employer Cannot discriminate against?
Employers cannot discriminate against employees or job applicants based on race, color, religion, sex, national origin, age (40 and older), disability, sexual orientation, gender identity, genetic information, or status as a protected veteran.
What are the different types of discrimination?
Discrimination can take many forms, such as race, color, religion, sex, national origin, age, and disability. These are all important factors that should be respected in any society.